In the modern day and age, the internet undoubtedly plays a significant role in almost every aspect of the world. Overall network of billions of users and a 200 exabyte data transfer rate per month makes the internet one of the most used entities in the whole world. We are no stranger to the internet either as our whole channel our presence etc is mostly based on the internet. Neither are you, I mean you are using the internet too right?? Reading this article and following up on the latest trends using the internet. A common way of accessing the internet is using an internet browser. There are other ways such as using terminal commands but that’s none of our business and we are going to focus on the browser here.
An internet browser, also known as a web browser, is a software application that is used to access and view web pages, documents, and other content on the internet. It provides a graphical user interface (GUI) for users to interact with web pages and navigate through them using hyperlinks, bookmarks, and other features.
Common examples of internet browsers include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Edge, Apple Safari, and Opera. Each browser may have its own unique features, but they all allow users to access and interact with web content through a familiar and easy-to-use interface.
When a user enters a web address (URL) into the browser’s address bar or clicks on a hyperlink, the browser sends a request to the web server hosting the content, which then sends the requested data back to the browser for display on the user’s device. Browsers also support various web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, allowing web developers to create dynamic and interactive web content. Browsers compete with each other trying to gain more market share by attracting user bases and monetizing their product by ad revenues and built-in premium features. Most browsers are backed by large tech-corporate entities causing them to gain leverage on sales and marketing. Chrome by google, safari by apple and edge by Microsoft. All these backed by a multi-billion dollar tech company. But tor browser is unlike any of them. As most browsers by default utilize search engines like google, bing, yahoo etc, tor doesn’t really promote a search engine. As most search engines can only implement surface web content.
The normal browser and the Tor browser work differently in terms of how they connect to and access the internet.
A normal browser such as Google Chrome or Mozilla Firefox connects to the internet directly through your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and sends requests for web pages and other content directly to the servers hosting that content. The requests and the resulting data are sent back and forth in clear text, which means that anyone who intercepts the traffic can potentially see what you’re doing and where you’re going on the internet.
The Tor browser, on the other hand, works by routing your internet traffic through a network of servers operated by volunteers around the world. This network of servers is called the Tor network, and it is designed to provide a high level of anonymity and privacy for users. When you use the Tor browser, your traffic is encrypted and sent through multiple servers in the network, making it very difficult for anyone to trace the traffic back to your device or location.
In addition to this, the Tor browser also disables certain features that can be used to track user activity, such as cookies and scripts, and it blocks access to certain types of content that could be used to compromise a user’s anonymity or privacy.
Overall, the Tor browser provides a higher level of privacy and anonymity than a normal browser, but it can also be slower and less convenient to use, as some websites and services may be blocked or require additional steps to access.
History of tor browser
The Tor browser is a free and open-source web browser that is designed to provide users with a high level of privacy and anonymity while browsing the internet. The development of the Tor browser can be traced back to the mid-1990s, when the U.S. Navy began work on a project called “Onion Routing” as a way to protect government communications over the internet.
Onion Routing was designed to provide a way to route internet traffic through multiple servers in order to make it difficult to trace the origin of the traffic. The idea was that each server in the chain would only be able to see the server that the traffic came from and the server that the traffic was going to, but not the originator of the traffic.
In 2002, the Tor Project was founded by computer scientists Roger Dingledine and Nick Mathewson, along with Paul Syverson of the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory. The Tor Project took the Onion Routing concept and expanded it into a global network of servers that could be used by anyone to protect their privacy and anonymity on the internet.
The name “Tor” stands for “The Onion Router”, which is a reference to the layered encryption used to protect user data as it passes through the network. The Tor network is made up of thousands of volunteer-run servers around the world, known as “nodes”, that work together to route internet traffic through the network.
The Tor browser itself is based on the Mozilla Firefox browser, with additional privacy and security features built in. When a user connects to the Tor network using the browser, their traffic is encrypted and sent through multiple servers in the network, making it very difficult for anyone to trace the traffic back to the user’s location or device.
Since its inception, the Tor browser has been used by a variety of people, including journalists, activists, and whistleblowers, to protect their online privacy and security. However, the Tor network has also been used by criminals and other malicious actors for illegal activities, such as selling drugs, distributing child pornography, and coordinating cyber attacks.
Despite these challenges, the Tor Project continues to work on improving the network and the browser, and has received funding from various sources, including the U.S. government, non-profit organizations, and individual donors.
How tor browser works
Tor Browser routes all your web traffic through the Tor network. The network in terms helps anonymize your activity by hiding traffic and altering user info relayed to the site itself. Tor consists of a three-layer proxy networking system, like layers of an onion. This system inspires the tor onion logo and their custom domains that end with .onion. Tor Browser connects to a random public listed entry node, then bounces that traffic through another randomized selected middle relay node and then finally spits out your traffic through the third and final exit node.
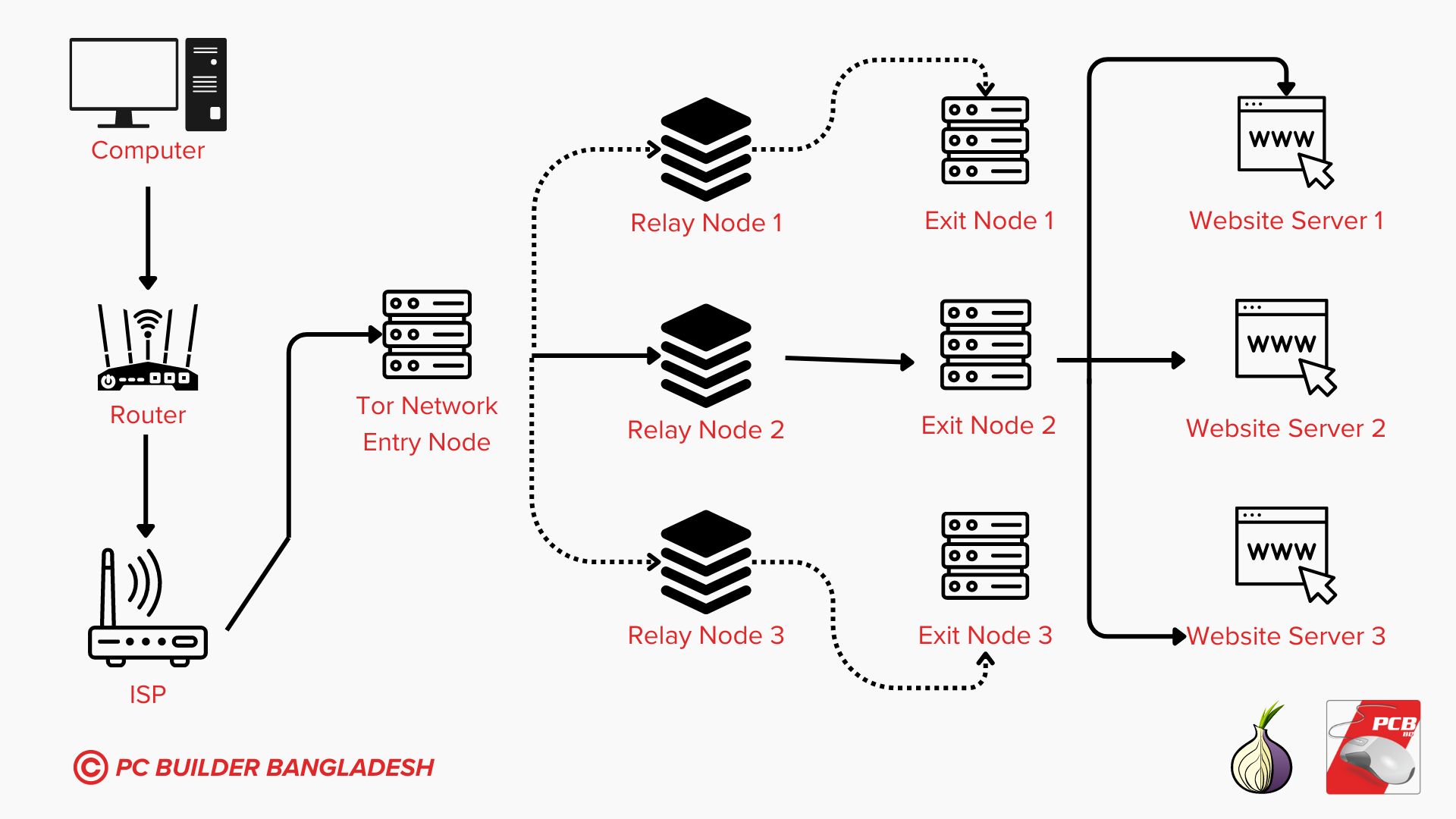
In this way of particular networking, the nodes do not know each others information. They just relay it. It is similar to how an onion works. The outer shell knows about the environment but nothing about the core while the inner shell knows about the core but nothing about the outside while the middle layer is just there to pass substances. Similarly the entry node gathers information about the computer but passes it through a proxy network and then the relay node which then passes/relays the information to multiple proxy networks as a hash that then gets transferred to the exit node and finally the designated site. All these can cause the experience of tor browser to be very laggy but it is worth it in the end.
Demerits of the tor browser
While the Tor browser provides a high level of privacy and anonymity, there are also some potential demerits or disadvantages to using it. Here are a few:
- Slow browsing speeds: Due to the way the Tor network works, browsing speeds can be significantly slower compared to a normal browser. This is because your traffic is routed through multiple servers, which can add extra latency and slow down the loading of web pages.
- Blocked websites: Some websites may block access to users coming from the Tor network, as it is often used by malicious actors for illegal activities. This can be frustrating for users who are trying to access legitimate content.
- Limited functionality: The Tor browser disables certain features that could be used to track user activity or compromise their privacy, such as cookies and scripts. This can result in some websites not functioning properly or requiring additional steps to access.
- Potential security risks: While the Tor network is designed to provide anonymity and privacy, it is not foolproof, and there have been instanc

The internet iceberg es where user data has been compromised or deanonymized. Additionally, some malicious actors have set up fake Tor exit nodes in order to intercept traffic and steal data.
- False sense of security: The Tor browser can provide a false sense of security to users, leading them to believe that their online activities are completely private and untraceable. While the Tor network can make it much more difficult to track user activity, it is not a guarantee of complete anonymity, and users should still exercise caution when using the internet.
Merits of the tor browser
The Tor browser is a popular tool for ensuring online privacy and anonymity. It provides several merits and benefits to users who are concerned about their online privacy and security. Here are some of the main merits of using Tor browser:
- Privacy and anonymity: The main benefit of using Tor browser is that it allows users to browse the internet anonymously. When a user connects to the Tor network, their traffic is routed through multiple servers, making it difficult for anyone to trace the traffic back to the user’s device or location. This makes it an excellent tool for protecting your online privacy and anonymity.
- Security: In addition to providing privacy and anonymity, the Tor browser also provides security benefits. The Tor network encrypts user traffic, making it difficult for anyone to intercept or eavesdrop on the traffic. This can help protect users from hacking attempts, phishing attacks, and other online threats.
- Access to censored content: The Tor browser allows users to access websites and content that may be censored or blocked in their country or region. Because the traffic is routed through multiple servers, it is difficult for governments or other authorities to block access to Tor network sites.
- Protection from tracking: The Tor browser can help protect users from online tracking and profiling. Because the Tor network obscures the user’s IP address and location, it makes it difficult for companies and advertisers to track their online activity and build a profile of their interests and preferences.
- Community-driven development: The Tor browser is developed by a community of volunteers and non-profit organizations, rather than a large corporation or government entity. This community-driven development model helps ensure that the software is designed with user privacy and security in mind.
Overall, the Tor browser is a powerful tool for protecting your online privacy and security. While it does have some limitations and potential drawbacks, the benefits it provides make it a valuable resource for anyone who wants to keep their online activity private and secure.
Is tor browser legal
The Tor browser is legal to use in most countries, including the United States and many European countries. However, in some countries, the use of Tor and other privacy tools may be restricted or illegal.
In countries with strict internet censorship or surveillance, the use of Tor may be seen as a way to circumvent government control or monitoring, and could result in legal repercussions. Additionally, the use of Tor for illegal activities, such as accessing child pornography or conducting cyber attacks, is illegal and can result in serious legal consequences.
It’s important to note that while using Tor browser is legal, it does not provide complete protection from the law. If a user engages in illegal activities while using Tor, they can still be identified and prosecuted.
In some cases, law enforcement agencies may be able to trace Tor traffic back to the user’s device, particularly if the user makes mistakes or uses Tor in an insecure manner. Additionally, in some countries, law enforcement agencies may monitor Tor traffic as part of their efforts to combat illegal activities.
Overall, while the use of Tor browser is legal in most countries, it’s important for users to be aware of the potential legal risks and to use the tool responsibly and ethically.
How to install the tor browser
Even after all the controversies and discussed dangers in using the tor browser, it is still a very powerful tool to use. In order to download the tor browser, you can follow the mentioned steps:
Here is the official site for an installation guide.
For Windows
- Navigate to the Tor Browser download page.
- Download the Windows .exe file.
- (Recommended) Verify the file’s signature.
- When the download is complete, double click the .exe file. Complete the installation wizard process.
For macOS
- Navigate to the Tor Browser download page.
- Download the macOS .dmg file.
- (Recommended) Verify the file’s signature.
- When the download is complete, double click the .dmg file. Complete the installation wizard process.
For GNU/Linux
- Navigate to the Tor Browser download page.
- Download the GNU/Linux .tar.xz file.
- (Recommended) Verify the file’s signature.
- Now follow either the graphical or the command-line method:
Graphical method
- When the download is complete, extract the archive using an archive manager.
- You’ll need to tell your GNU/Linux that you want the ability to execute shell scripts. Navigate to the newly extracted Tor Browser directory. Right click on start-tor-browser.desktop, open Properties or Preferences and change the permission to allow executing file as program. Double-click the icon to start up Tor Browser for the first time.
Note: On Ubuntu and some other distros if you try to launch start-tor-browser.desktop a text file might open up. To change this behavior and launch Tor Browser instead, follow this:
- Launch “Files” (GNOME Files/Nautilus)
- Click on Preferences.
- Navigate to the ‘Behavior’ Tab.
- Select “Run them” or “Ask what to do” under “Executable Text Files”.
- If you choose the latter click on “Run” after launching the start-tor-browser.desktop file.
Command-line method
- When the download is complete, extract the archive with the command tar -xf [TB archive].
- From inside the Tor Browser directory, you can launch Tor Browser by running:
./start-tor-browser.desktop
Note: If this command fails to run, you probably need to make the file executable. From within this directory run: chmod +x start-tor-browser.desktop
Some additional flags that can be used with start-tor-browser.desktop from the command-line:
| Flag | Description |
| –register-app | To register Tor Browser as a desktop application. |
| –verbose | To display Tor and Firefox output in the terminal. |
| –log [file] | To record Tor and Firefox output in file (default: tor-browser.log). |
| –detach | To detach from terminal and run Tor Browser in the background. |
| –unregister-app | To unregister Tor Browser as a desktop application. |
About .onion sites
.onion sites are websites that can only be accessed through the Tor network using the Tor browser. These sites are not indexed by search engines and their URLs are usually a random string of letters and numbers followed by the “.onion” domain extension.
.onion sites are often associated with illegal activities, such as drug sales, hacking forums, and black market websites. However, there are also legitimate uses for .onion sites, such as anonymous blogging, whistleblowing, and secure communication.
Because .onion sites are only accessible through the Tor network, they offer a high level of anonymity and privacy for both website owners and visitors. The Tor network obscures the user’s IP address and location, making it difficult for anyone to trace their online activity.
However, it’s important to note that while .onion sites offer a degree of anonymity, they are not completely secure or untraceable. Law enforcement agencies have been able to track down and shut down some .onion sites in the past, and users should not assume that their activity on these sites is completely anonymous or untraceable.
Additionally, because .onion sites are not indexed by search engines, it can be difficult to find legitimate sites without knowing the URL in advance. Some resources exist for finding .onion sites, such as directories and search engines specifically designed for the Tor network.
Overall, .onion sites offer a high level of anonymity and privacy, but they also carry potential risks and users should exercise caution when accessing and using these sites.
Dark Web search engines
The most popular search engines like google, bing do not work in the tor browser. You can access the domains but in most cases you will get captchas because google and bing tends to block the ip’s. With tor browser the default browser is duckduckgo. But it cannot index onion sites. So, there are some indie search engines that index onion sites but please visit these with caution. Due to monetization and family friendly reasons we cannot mention the search engines. These search engines are very dangerous as they can contain links to various illegal sites and no one has control to it as the sites are manually indexed not scraped like google or bing.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Tor browser is a powerful tool that can provide users with a high level of online privacy and security. It allows users to browse the internet anonymously and securely, protecting them from online tracking, profiling, and surveillance. The Tor network also provides access to content that may be censored or blocked in certain countries or regions.
However, it’s important to note that while the Tor browser can provide a degree of anonymity and security, it is not foolproof and users should not assume that their online activity is completely anonymous or untraceable. Additionally, the use of Tor for illegal activities is illegal and can result in serious legal consequences.
Overall, the Tor browser is a valuable tool for anyone who values their online privacy and security, but users should use it responsibly and ethically, and be aware of its potential limitations and risks.






